This post is used to log my leetcode problem solving.
2785. Sort Vowels in a String 2025.09.11
Given a 0-indexed string s, permute s to get a new string t such that:
- All consonants remain in their original places. More formally, if there is an index
iwith0 <= i < s.lengthsuch thats[i]is a consonant, thent[i] = s[i]. - The vowels must be sorted in the nondecreasing order of their ASCII values. More formally, for pairs of indices
i,jwith0 <= i < j < s.lengthsuch thats[i]ands[j]are vowels, thent[i]must not have a higher ASCII value thant[j].
Return the resulting string.
The vowels are 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', and 'u', and they can appear in lowercase or uppercase. Consonants comprise all letters that are not vowels.
Example 1:
Input: s = “lEetcOde”
Output: “lEOtcede”
Explanation: ‘E’, ‘O’, and ’e’ are the vowels in s; ’l’, ’t’, ‘c’, and ’d’ are all consonants. The vowels are sorted according to their ASCII values, and the consonants remain in the same places.
Example 2:
Input: s = “lYmpH”
Output: “lYmpH”
Explanation: There are no vowels in s (all characters in s are consonants), so we return “lYmpH”.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105sconsists only of letters of the English alphabet in uppercase and lowercase.
Solution
| |
3227. Vowels Game in a String 2025.09.12
Alice and Bob are playing a game on a string.
You are given a string s, Alice and Bob will take turns playing the following game where Alice starts first:
- On Alice’s turn, she has to remove any non-empty substring from
sthat contains an odd number of vowels. - On Bob’s turn, he has to remove any non-empty substring from
sthat contains an even number of vowels.
The first player who cannot make a move on their turn loses the game. We assume that both Alice and Bob play optimally.
Return true if Alice wins the game, and false otherwise.
The English vowels are: a, e, i, o, and u.
Example 1:
Input: s = “leetcoder”
Output: true
Explanation:
Alice can win the game as follows:
- Alice plays first, she can delete the underlined substring in
s = "**leetco**der"which contains 3 vowels. The resulting string iss = "der". - Bob plays second, he can delete the underlined substring in
s = "**d**er"which contains 0 vowels. The resulting string iss = "er". - Alice plays third, she can delete the whole string
s = "**er**"which contains 1 vowel. - Bob plays fourth, since the string is empty, there is no valid play for Bob. So Alice wins the game.
Example 2:
Input: s = “bbcd”
Output: false
Explanation:
There is no valid play for Alice in her first turn, so Alice loses the game.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Solution
Consider only the number of vowels. If the number of vowels is 0, Alice fails. If it’s odd, Alice could remove the whole string, Alice wins. If it’s even, after removing odd number of vowels, the remaining number is odd, Alice wins.
| |
3541. Find Most Frequent Vowel and Consonant 2025.09.13
You are given a string s consisting of lowercase English letters ('a' to 'z').
Your task is to:
- Find the vowel (one of
'a','e','i','o', or'u') with the maximum frequency. - Find the consonant (all other letters excluding vowels) with the maximum frequency.
Return the sum of the two frequencies.
Note: If multiple vowels or consonants have the same maximum frequency, you may choose any one of them. If there are no vowels or no consonants in the string, consider their frequency as 0.
The frequency of a letter x is the number of times it occurs in the string.
Example 1:
Input: s = “successes”
Output: 6
Explanation:
- The vowels are:
'u'(frequency 1),'e'(frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 2. - The consonants are:
's'(frequency 4),'c'(frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 4. - The output is
2 + 4 = 6.
Example 2:
Input: s = “aeiaeia”
Output: 3
Explanation:
- The vowels are:
'a'(frequency 3),'e'( frequency 2),'i'(frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 3. - There are no consonants in
s. Hence, maximum consonant frequency = 0. - The output is
3 + 0 = 3.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 100sconsists of lowercase English letters only.
Solution
| |
966. Vowel Spellchecker 2025.09.14
Given a wordlist, we want to implement a spellchecker that converts a query word into a correct word.
For a given query word, the spell checker handles two categories of spelling mistakes:
- Capitalization: If the query matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the case in the wordlist.
- Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "YellOw":correct = "yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["Yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "Yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "yellow"
- Example:
- Vowel Errors: If after replacing the vowels
('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u')of the query word with any vowel individually, it matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the match in the wordlist.- Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yollow":correct = "YellOw" - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yeellow":correct = ""(no match) - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yllw":correct = ""(no match)
- Example:
In addition, the spell checker operates under the following precedence rules:
- When the query exactly matches a word in the wordlist (case-sensitive), you should return the same word back.
- When the query matches a word up to capitlization, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- When the query matches a word up to vowel errors, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- If the query has no matches in the wordlist, you should return the empty string.
Given some queries, return a list of words answer, where answer[i] is the correct word for query = queries[i].
Example 1:
Input: wordlist = [“KiTe”,“kite”,“hare”,“Hare”], queries = [“kite”,“Kite”,“KiTe”,“Hare”,“HARE”,“Hear”,“hear”,“keti”,“keet”,“keto”] Output: [“kite”,“KiTe”,“KiTe”,“Hare”,“hare”,"","",“KiTe”,"",“KiTe”]
Example 2:
Input: wordlist = [“yellow”], queries = [“YellOw”] Output: [“yellow”]
Constraints:
1 <= wordlist.length, queries.length <= 50001 <= wordlist[i].length, queries[i].length <= 7wordlist[i]andqueries[i]consist only of only English letters.
Solution
First Try: save all matches in one hashmap and extract by priority (TLE in some testcases)
| |
Optimized by Gemini: Save results in three different hashmaps and lookup hashmap by priority
| |
1935. Maximum Number of Words You Can Type 2025.09.15
There is a malfunctioning keyboard where some letter keys do not work. All other keys on the keyboard work properly.
Given a string text of words separated by a single space (no leading or trailing spaces) and a string brokenLetters of all distinct letter keys that are broken, return the number of words in text you can fully type using this keyboard.
Example 1:
Input: text = “hello world”, brokenLetters = “ad” Output: 1 Explanation: We cannot type “world” because the ’d’ key is broken.
Example 2:
Input: text = “leet code”, brokenLetters = “lt” Output: 1 Explanation: We cannot type “leet” because the ’l’ and ’t’ keys are broken.
Example 3:
Input: text = “leet code”, brokenLetters = “e” Output: 0 Explanation: We cannot type either word because the ’e’ key is broken.
Constraints:
1 <= text.length <= 1040 <= brokenLetters.length <= 26textconsists of words separated by a single space without any leading or trailing spaces.- Each word only consists of lowercase English letters.
brokenLettersconsists of distinct lowercase English letters.
Solution
| |
2197. Replace Non-Coprime Numbers in Array 2025.09.16
You are given an array of integers nums. Perform the following steps:
- Find any two adjacent numbers in
numsthat are non-coprime. - If no such numbers are found, stop the process.
- Otherwise, delete the two numbers and replace them with their LCM (Least Common Multiple).
- Repeat this process as long as you keep finding two adjacent non-coprime numbers.
Return the final modified array. It can be shown that replacing adjacent non-coprime numbers in any arbitrary order will lead to the same result.
The test cases are generated such that the values in the final array are less than or equal to 108.
Two values x and y are non-coprime if GCD(x, y) > 1 where GCD(x, y) is the Greatest Common Divisor of x and y.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [6,4,3,2,7,6,2] Output: [12,7,6] Explanation:
- (6, 4) are non-coprime with LCM(6, 4) = 12. Now, nums = [12,3,2,7,6,2].
- (12, 3) are non-coprime with LCM(12, 3) = 12. Now, nums = [12,2,7,6,2].
- (12, 2) are non-coprime with LCM(12, 2) = 12. Now, nums = [12,7,6,2].
- (6, 2) are non-coprime with LCM(6, 2) = 6. Now, nums = [12,7,6]. There are no more adjacent non-coprime numbers in nums. Thus, the final modified array is [12,7,6]. Note that there are other ways to obtain the same resultant array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,1,1,3,3,3] Output: [2,1,1,3] Explanation:
- (3, 3) are non-coprime with LCM(3, 3) = 3. Now, nums = [2,2,1,1,3,3].
- (3, 3) are non-coprime with LCM(3, 3) = 3. Now, nums = [2,2,1,1,3].
- (2, 2) are non-coprime with LCM(2, 2) = 2. Now, nums = [2,1,1,3]. There are no more adjacent non-coprime numbers in nums. Thus, the final modified array is [2,1,1,3]. Note that there are other ways to obtain the same resultant array.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105- The test cases are generated such that the values in the final array are less than or equal to
108.
Solution
Intuitive solution, followed by instructions in the description, but fails by TLE on some testcases
| |
Optimized by Claude by stack
| |
2353. Design a Food Rating System 2025.09.17
Design a food rating system that can do the following:
- Modify the rating of a food item listed in the system.
- Return the highest-rated food item for a type of cuisine in the system.
Implement the FoodRatings class:
FoodRatings(String[] foods, String[] cuisines, int[] ratings)Initializes the system. The food items are described byfoods,cuisinesandratings, all of which have a length ofn.foods[i]is the name of theithfood,cuisines[i]is the type of cuisine of theithfood, andratings[i]is the initial rating of theithfood.
void changeRating(String food, int newRating)Changes the rating of the food item with the namefood.String highestRated(String cuisine)Returns the name of the food item that has the highest rating for the given type ofcuisine. If there is a tie, return the item with the lexicographically smaller name.
Note that a string x is lexicographically smaller than string y if x comes before y in dictionary order, that is, either x is a prefix of y, or if i is the first position such that x[i] != y[i], then x[i] comes before y[i] in alphabetic order.
Example 1:
Input
[“FoodRatings”, “highestRated”, “highestRated”, “changeRating”, “highestRated”, “changeRating”, “highestRated”]
[[[“kimchi”, “miso”, “sushi”, “moussaka”, “ramen”, “bulgogi”], [“korean”, “japanese”, “japanese”, “greek”, “japanese”, “korean”], [9, 12, 8, 15, 14, 7]], [“korean”], [“japanese”], [“sushi”, 16], [“japanese”], [“ramen”, 16], [“japanese”]]
Output
[null, “kimchi”, “ramen”, null, “sushi”, null, “ramen”]
Explanation
FoodRatings foodRatings = new FoodRatings([“kimchi”, “miso”, “sushi”, “moussaka”, “ramen”, “bulgogi”], [“korean”, “japanese”, “japanese”, “greek”, “japanese”, “korean”], [9, 12, 8, 15, 14, 7]);
foodRatings.highestRated(“korean”); // return “kimchi”
// “kimchi” is the highest rated korean food with a rating of 9.
foodRatings.highestRated(“japanese”); // return “ramen”
// “ramen” is the highest rated japanese food with a rating of 14.
foodRatings.changeRating(“sushi”, 16); // “sushi” now has a rating of 16.
foodRatings.highestRated(“japanese”); // return “sushi”
// “sushi” is the highest rated japanese food with a rating of 16.
foodRatings.changeRating(“ramen”, 16); // “ramen” now has a rating of 16.
foodRatings.highestRated(“japanese”); // return “ramen”
// Both “sushi” and “ramen” have a rating of 16.
// However, “ramen” is lexicographically smaller than “sushi”.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104n == foods.length == cuisines.length == ratings.length1 <= foods[i].length, cuisines[i].length <= 10foods[i],cuisines[i]consist of lowercase English letters.1 <= ratings[i] <= 108- All the strings in
foodsare distinct. foodwill be the name of a food item in the system across all calls tochangeRating.cuisinewill be a type of cuisine of at least one food item in the system across all calls tohighestRated.- At most
2 * 104calls in total will be made tochangeRatingandhighestRated.
Solution
Direct implementation by lists. $\mathcal O(n)$ time complexity. TLE on some testcases
| |
Optimized by hashtable and heap
| |
3408. Design Task Manager 2025.09.18
There is a task management system that allows users to manage their tasks, each associated with a priority. The system should efficiently handle adding, modifying, executing, and removing tasks.
Implement the TaskManager class:
TaskManager(vector<vector<int>>& tasks)initializes the task manager with a list of user-task-priority triples. Each element in the input list is of the form[userId, taskId, priority], which adds a task to the specified user with the given priority.void add(int userId, int taskId, int priority)adds a task with the specifiedtaskIdandpriorityto the user withuserId. It is guaranteed thattaskIddoes not exist in the system.void edit(int taskId, int newPriority)updates the priority of the existingtaskIdtonewPriority. It is guaranteed thattaskIdexists in the system.void rmv(int taskId)removes the task identified bytaskIdfrom the system. It is guaranteed thattaskIdexists in the system.int execTop()executes the task with the highest priority across all users. If there are multiple tasks with the same highest priority, execute the one with the highesttaskId. After executing, thetaskIdis removed from the system. Return theuserIdassociated with the executed task. If no tasks are available, return -1.
Note that a user may be assigned multiple tasks.
Example 1:
Input:
[“TaskManager”, “add”, “edit”, “execTop”, “rmv”, “add”, “execTop”]
[[[[1, 101, 10], [2, 102, 20], [3, 103, 15]]], [4, 104, 5], [102, 8], [], [101], [5, 105, 15], []]
Output:
[null, null, null, 3, null, null, 5]
Explanation
TaskManager taskManager = new TaskManager([[1, 101, 10], [2, 102, 20], [3, 103, 15]]); // Initializes with three tasks for Users 1, 2, and 3.
taskManager.add(4, 104, 5); // Adds task 104 with priority 5 for User 4.
taskManager.edit(102, 8); // Updates priority of task 102 to 8.
taskManager.execTop(); // return 3. Executes task 103 for User 3.
taskManager.rmv(101); // Removes task 101 from the system.
taskManager.add(5, 105, 15); // Adds task 105 with priority 15 for User 5.
taskManager.execTop(); // return 5. Executes task 105 for User 5.
Constraints:
1 <= tasks.length <= 1050 <= userId <= 1050 <= taskId <= 1050 <= priority <= 1090 <= newPriority <= 109- At most
2 * 105calls will be made in total toadd,edit,rmv, andexecTopmethods. - The input is generated such that
taskIdwill be valid.
Solution
Similar to last daily problem. Use a hashmap to store all tasks and a heap to store priority with lazy cleanup.
| |
3484. Design Spreadsheet 2025.09.19
A spreadsheet is a grid with 26 columns (labeled from 'A' to 'Z') and a given number of rows. Each cell in the spreadsheet can hold an integer value between 0 and 105.
Implement the Spreadsheet class:
Spreadsheet(int rows)Initializes a spreadsheet with 26 columns (labeled'A'to'Z') and the specified number of rows. All cells are initially set to 0.void setCell(String cell, int value)Sets the value of the specifiedcell. The cell reference is provided in the format"AX"(e.g.,"A1","B10"), where the letter represents the column (from'A'to'Z') and the number represents a 1-indexed row.void resetCell(String cell)Resets the specified cell to 0.int getValue(String formula)Evaluates a formula of the form"=X+Y", whereXandYare either cell references or non-negative integers, and returns the computed sum.
Note: If getValue references a cell that has not been explicitly set using setCell, its value is considered 0.
Example 1:
Input:
[“Spreadsheet”, “getValue”, “setCell”, “getValue”, “setCell”, “getValue”, “resetCell”, “getValue”]
[[3], ["=5+7"], [“A1”, 10], ["=A1+6"], [“B2”, 15], ["=A1+B2"], [“A1”], ["=A1+B2"]]
Output:
[null, 12, null, 16, null, 25, null, 15]
Explanation
Spreadsheet spreadsheet = new Spreadsheet(3); // Initializes a spreadsheet with 3 rows and 26 columns
spreadsheet.getValue("=5+7"); // returns 12 (5+7)
spreadsheet.setCell(“A1”, 10); // sets A1 to 10
spreadsheet.getValue("=A1+6"); // returns 16 (10+6)
spreadsheet.setCell(“B2”, 15); // sets B2 to 15
spreadsheet.getValue("=A1+B2"); // returns 25 (10+15)
spreadsheet.resetCell(“A1”); // resets A1 to 0
spreadsheet.getValue("=A1+B2"); // returns 15 (0+15)
Constraints:
1 <= rows <= 1030 <= value <= 105- The formula is always in the format
"=X+Y", whereXandYare either valid cell references or non-negative integers with values less than or equal to105. - Each cell reference consists of a capital letter from
'A'to'Z'followed by a row number between1androws. - At most
104calls will be made in total tosetCell,resetCell, andgetValue.
Solution
Solution1: use nested lists
| |
Solution2: use hashtable
| |
3508. Implement Router 2025.09.21
Design a data structure that can efficiently manage data packets in a network router. Each data packet consists of the following attributes:
source: A unique identifier for the machine that generated the packet.destination: A unique identifier for the target machine.timestamp: The time at which the packet arrived at the router.
Implement the Router class:
Router(int memoryLimit): Initializes the Router object with a fixed memory limit.
memoryLimitis the maximum number of packets the router can store at any given time.- If adding a new packet would exceed this limit, the oldest packet must be removed to free up space.
bool addPacket(int source, int destination, int timestamp): Adds a packet with the given attributes to the router.
- A packet is considered a duplicate if another packet with the same
source,destination, andtimestampalready exists in the router. - Return
trueif the packet is successfully added (i.e., it is not a duplicate); otherwise returnfalse.
int[] forwardPacket(): Forwards the next packet in FIFO (First In First Out) order.
- Remove the packet from storage.
- Return the packet as an array
[source, destination, timestamp]. - If there are no packets to forward, return an empty array.
int getCount(int destination, int startTime, int endTime):
- Returns the number of packets currently stored in the router (i.e., not yet forwarded) that have the specified destination and have timestamps in the inclusive range
[startTime, endTime].
Note that queries for addPacket will be made in increasing order of timestamp.
Example 1:
Input:
[“Router”, “addPacket”, “addPacket”, “addPacket”, “addPacket”, “addPacket”, “forwardPacket”, “addPacket”, “getCount”]
[[3], [1, 4, 90], [2, 5, 90], [1, 4, 90], [3, 5, 95], [4, 5, 105], [], [5, 2, 110], [5, 100, 110]]
Output:
[null, true, true, false, true, true, [2, 5, 90], true, 1]
Explanation
Router router = new Router(3); // Initialize Router with memoryLimit of 3.
router.addPacket(1, 4, 90); // Packet is added. Return True.
router.addPacket(2, 5, 90); // Packet is added. Return True.
router.addPacket(1, 4, 90); // This is a duplicate packet. Return False.
router.addPacket(3, 5, 95); // Packet is added. Return True
router.addPacket(4, 5, 105); // Packet is added, [1, 4, 90] is removed as number of packets exceeds memoryLimit. Return True.
router.forwardPacket(); // Return [2, 5, 90] and remove it from router.
router.addPacket(5, 2, 110); // Packet is added. Return True.
router.getCount(5, 100, 110); // The only packet with destination 5 and timestamp in the inclusive range [100, 110] is [4, 5, 105]. Return 1.
Example 2:
Input:
[“Router”, “addPacket”, “forwardPacket”, “forwardPacket”]
[[2], [7, 4, 90], [], []]
Output:
[null, true, [7, 4, 90], []]
Explanation
Router router = new Router(2); // Initialize Router with memoryLimit of 2.
router.addPacket(7, 4, 90); // Return True.
router.forwardPacket(); // Return [7, 4, 90].
router.forwardPacket(); // There are no packets left, return [].
Constraints:
2 <= memoryLimit <= 1051 <= source, destination <= 2 * 1051 <= timestamp <= 1091 <= startTime <= endTime <= 109- At most
105calls will be made toaddPacket,forwardPacket, andgetCountmethods altogether. - queries for
addPacketwill be made in increasing order oftimestamp.
Solution
Implement by stack, TLE on some testcases
| |
Optimzied by binary search
| |
3005. Count Elements With Maximum Frequency 2025.09.22
You are given an array nums consisting of positive integers.
Return the total frequencies of elements in nums such that those elements all have the maximum frequency.
The frequency of an element is the number of occurrences of that element in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,2,3,1,4]
Output: 4
Explanation: The elements 1 and 2 have a frequency of 2 which is the maximum frequency in the array.
So the number of elements in the array with maximum frequency is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 5
Explanation: All elements of the array have a frequency of 1 which is the maximum.
So the number of elements in the array with maximum frequency is 5.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1001 <= nums[i] <= 100
| |
165. Compare Version Numbers 2025.09.23
Given two version strings, version1 and version2, compare them. A version string consists of revisions separated by dots '.'. The value of the revision is its integer conversion ignoring leading zeros.
To compare version strings, compare their revision values in left-to-right order. If one of the version strings has fewer revisions, treat the missing revision values as 0.
Return the following:
- If
version1 < version2, return -1. - If
version1 > version2, return 1. - Otherwise, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: version1 = “1.2”, version2 = “1.10”
Output: -1
Explanation:
version1’s second revision is “2” and version2’s second revision is “10”: 2 < 10, so version1 < version2.
Example 2:
Input: version1 = “1.01”, version2 = “1.001”
Output: 0
Explanation:
Ignoring leading zeroes, both “01” and “001” represent the same integer “1”.
Example 3:
Input: version1 = “1.0”, version2 = “1.0.0.0”
Output: 0
Explanation:
version1 has less revisions, which means every missing revision are treated as “0”.
Constraints:
1 <= version1.length, version2.length <= 500version1andversion2only contain digits and'.'.version1andversion2are valid version numbers.- All the given revisions in
version1andversion2can be stored in a 32-bit integer.
Solution
Filling the trailing zeros and using tuple comparison
| |
166. Fraction to Recurring Decimal 2025.09.24
Given two integers representing the numerator and denominator of a fraction, return the fraction in string format.
If the fractional part is repeating, enclose the repeating part in parentheses.
If multiple answers are possible, return any of them.
It is guaranteed that the length of the answer string is less than 104 for all the given inputs.
Example 1:
Input: numerator = 1, denominator = 2 Output: “0.5”
Example 2:
Input: numerator = 2, denominator = 1 Output: “2”
Example 3:
Input: numerator = 4, denominator = 333 Output: “0.(012)”
Constraints:
-231 <= numerator, denominator <= 231 - 1denominator != 0
Solution
Similar to large number multiplication but be cautious of corner cases
| |
Optimize the time efficiency by replacing list with hashmap
| |
120. Triangle 2025.09.25
Given a triangle array, return the minimum path sum from top to bottom.
For each step, you may move to an adjacent number of the row below. More formally, if you are on index i on the current row, you may move to either index i or index i + 1 on the next row.
Example 1:
Input: triangle = [[2],[3,4],[6,5,7],[4,1,8,3]]
Output: 11
Explanation: The triangle looks like:
2
3 4
6 5 7
4 1 8 3
The minimum path sum from top to bottom is 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11 (underlined above).
Example 2:
Input: triangle = [[-10]]
Output: -10
Constraints:
1 <= triangle.length <= 200triangle[0].length == 1triangle[i].length == triangle[i - 1].length + 1-104 <= triangle[i][j] <= 104
Follow up: Could you do this using only O(n) extra space, where n is the total number of rows in the triangle?
Solution
Dynamic Planning
| |
611. Valid Triangle Number 2025.09.26
Given an integer array nums, return the number of triplets chosen from the array that can make triangles if we take them as side lengths of a triangle.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,4]
Output: 3
Explanation: Valid combinations are:
2,3,4 (using the first 2)
2,3,4 (using the second 2)
2,2,3
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,2,3,4]
Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
Solution
2 pointers
| |
812. Largest Triangle Area 2025.09.27
Given an array of points on the X-Y plane points where points[i] = [xi, yi], return the area of the largest triangle that can be formed by any three different points. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
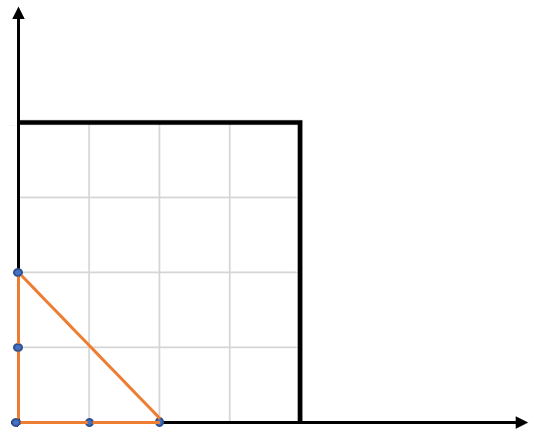
Input: points = [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[0,2],[2,0]]
Output: 2.00000
Explanation: The five points are shown in the above figure. The red triangle is the largest.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[1,0],[0,0],[0,1]]
Output: 0.50000
Constraints:
3 <= points.length <= 50-50 <= xi, yi <= 50- All the given points are unique.
Solution
brutal force loop
| |
976. Largest Perimeter Triangle 2025.09.28
Given an integer array nums, return the largest perimeter of a triangle with a non-zero area, formed from three of these lengths. If it is impossible to form any triangle of a non-zero area, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,1,2]
Output: 5
Explanation: You can form a triangle with three side lengths: 1, 2, and 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,1,10]
Output: 0
Explanation:
You cannot use the side lengths 1, 1, and 2 to form a triangle.
You cannot use the side lengths 1, 1, and 10 to form a triangle.
You cannot use the side lengths 1, 2, and 10 to form a triangle.
As we cannot use any three side lengths to form a triangle of non-zero area, we return 0.
Constraints:
3 <= nums.length <= 10^41 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
Solution
Greedy algorithm
| |
2221. Find Triangular Sum of an Array 2025.09.30
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a digit between 0 and 9 (inclusive).
The triangular sum of nums is the value of the only element present in nums after the following process terminates:
- Let
numscomprise ofnelements. Ifn == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer arraynewNumsof lengthn - 1. - For each index
i, where0 <= i < n - 1, assign the value ofnewNums[i]as(nums[i] + nums[i+1]) % 10, where%denotes modulo operator. - Replace the array
numswithnewNums. - Repeat the entire process starting from step 1.
Return the triangular sum of nums.
Example 1:
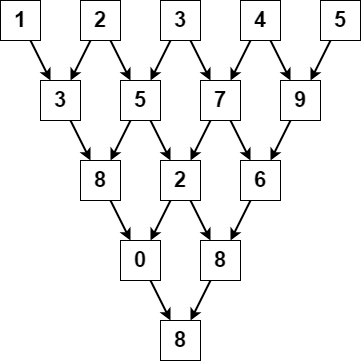
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 8
Explanation:
The above diagram depicts the process from which we obtain the triangular sum of the array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5]
Output: 5
Explanation:
Since there is only one element in nums, the triangular sum is the value of that element itself.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 9
Recurrsion
| |
1518. Water Bottles 2025.10.01
There are numBottles water bottles that are initially full of water. You can exchange numExchange empty water bottles from the market with one full water bottle.
The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle.
Given the two integers numBottles and numExchange, return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
Example 1:
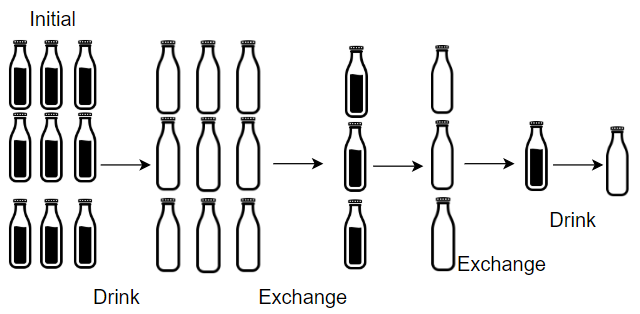
Input: numBottles = 9, numExchange = 3
Output: 13
Explanation: You can exchange 3 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle.
Number of water bottles you can drink: 9 + 3 + 1 = 13.
Example 2:
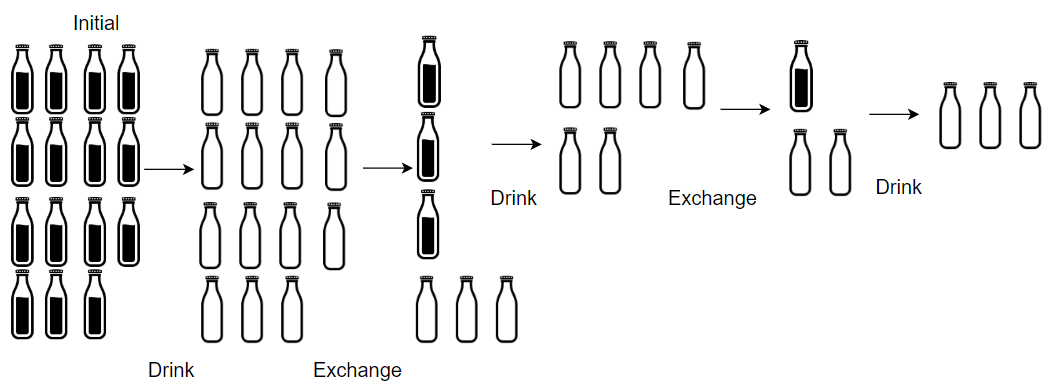
Input: numBottles = 15, numExchange = 4
Output: 19
Explanation: You can exchange 4 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle.
Number of water bottles you can drink: 15 + 3 + 1 = 19.
Constraints:
1 <= numBottles <= 1002 <= numExchange <= 100
Solution
Follow the instruction
| |
3100. Water Bottles II 2025.10.02
You are given two integers numBottles and numExchange.
numBottles represents the number of full water bottles that you initially have. In one operation, you can perform one of the following operations:
- Drink any number of full water bottles turning them into empty bottles.
- Exchange
numExchangeempty bottles with one full water bottle. Then, increasenumExchangeby one.
Note that you cannot exchange multiple batches of empty bottles for the same value of numExchange. For example, if numBottles == 3 and numExchange == 1, you cannot exchange 3 empty water bottles for 3 full bottles.
Return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
Example 1:
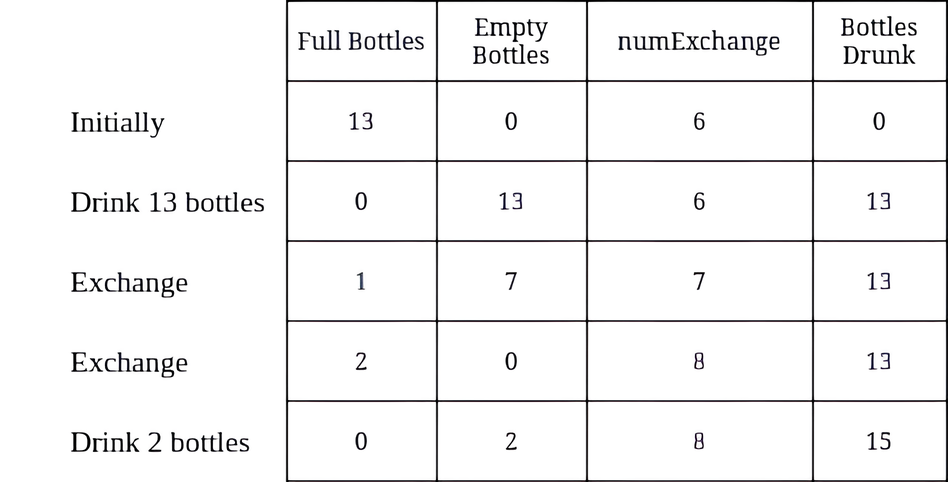
Input: numBottles = 13, numExchange = 6
Output: 15
Explanation: The table above shows the number of full water bottles, empty water bottles, the value of numExchange, and the number of bottles drunk.
Example 2:
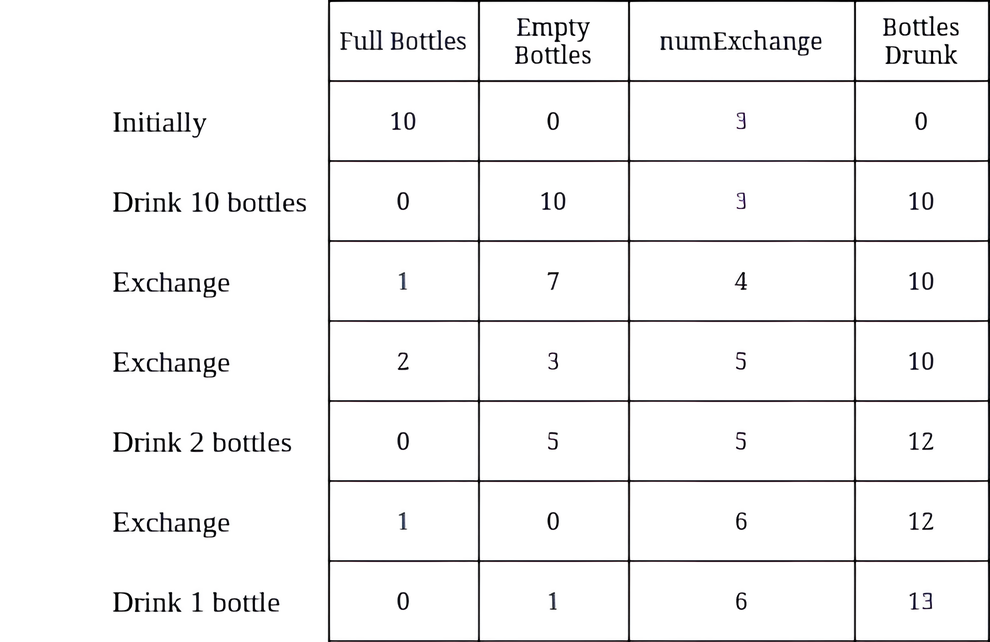
Input: numBottles = 10, numExchange = 3
Output: 13
Explanation: The table above shows the number of full water bottles, empty water bottles, the value of numExchange, and the number of bottles drunk.
Constraints:
1 <= numBottles <= 1001 <= numExchange <= 100
| |
417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow 2025.10.05
There is an m x n rectangular island that borders both the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean touches the island’s left and top edges, and the Atlantic Ocean touches the island’s right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an m x n integer matrix heights where heights[r][c] represents the height above sea level of the cell at coordinate (r, c).
The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell’s height is less than or equal to the current cell’s height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
Return a 2D list of grid coordinates result where result[i] = [ri, ci] denotes that rain water can flow from cell (ri, ci) to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
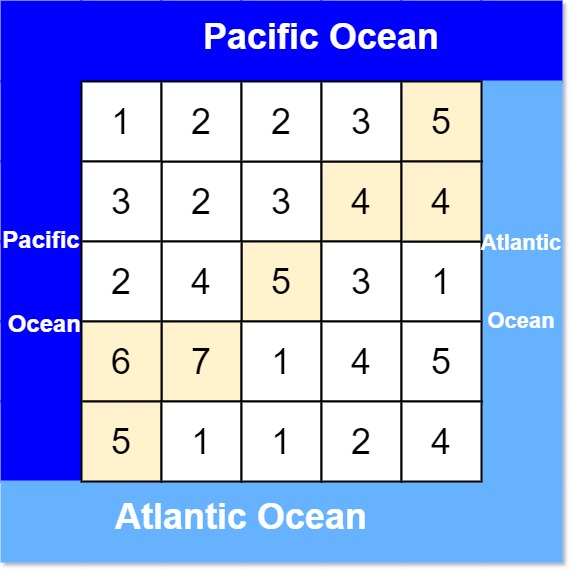
Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
Explanation: The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below:
[0,4]: [0,4] -> Pacific Ocean
[0,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,3]: [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,3] -> [1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[1,4]: [1,4] -> [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean
[1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[2,2]: [2,2] -> [1,2] -> [0,2] -> Pacific Ocean
[2,2] -> [2,3] -> [2,4] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,0]: [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,0] -> [4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean
[3,1]: [3,1] -> [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[3,1] -> [4,1] -> Atlantic Ocean
[4,0]: [4,0] -> Pacific Ocean
[4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean
Note that there are other possible paths for these cells to flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 2:
Input: heights = [[1]]
Output: [[0,0]]
Explanation: The water can flow from the only cell to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Constraints:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
Solution
DFS or BFS from different sides and find intersections
| |
2300. Successful Pairs of Spells and Potions 2025.10.08
You are given two positive integer arrays spells and potions, of length n and m respectively, where spells[i] represents the strength of the ith spell and potions[j] represents the strength of the jth potion.
You are also given an integer success. A spell and potion pair is considered successful if the product of their strengths is at least success.
Return an integer array pairs of length n where pairs[i] is the number of potions that will form a successful pair with the ith spell.
Example 1:
Input: spells = [5,1,3], potions = [1,2,3,4,5], success = 7
Output: [4,0,3]
Explanation:
- 0th spell: 5 * [1,2,3,4,5] = [5,10,15,20,25]. 4 pairs are successful.
- 1st spell: 1 * [1,2,3,4,5] = [1,2,3,4,5]. 0 pairs are successful.
- 2nd spell: 3 * [1,2,3,4,5] = [3,6,9,12,15]. 3 pairs are successful. Thus, [4,0,3] is returned.
Example 2:
Input: spells = [3,1,2], potions = [8,5,8], success = 16
Output: [2,0,2]
Explanation:
- 0th spell: 3 * [8,5,8] = [24,15,24]. 2 pairs are successful.
- 1st spell: 1 * [8,5,8] = [8,5,8]. 0 pairs are successful.
- 2nd spell: 2 * [8,5,8] = [16,10,16]. 2 pairs are successful. Thus, [2,0,2] is returned.
Constraints:
n == spells.lengthm == potions.length1 <= n, m <= 1051 <= spells[i], potions[i] <= 1051 <= success <= 1010
Solution
| |
| |
3186. Maximum Total Damage With Spell Casting 2025.10.11
A magician has various spells.
You are given an array power, where each element represents the damage of a spell. Multiple spells can have the same damage value.
It is a known fact that if a magician decides to cast a spell with a damage of power[i], they cannot cast any spell with a damage of power[i] - 2, power[i] - 1, power[i] + 1, or power[i] + 2.
Each spell can be cast only once.
Return the maximum possible total damage that a magician can cast.
Example 1:
Input: power = [1,1,3,4]
Output: 6
Explanation:
The maximum possible damage of 6 is produced by casting spells 0, 1, 3 with damage 1, 1, 4.
Example 2:
Input: power = [7,1,6,6]
Output: 13
Explanation:
The maximum possible damage of 13 is produced by casting spells 1, 2, 3 with damage 1, 6, 6.
Constraints:
1 <= power.length <= 1051 <= power[i] <= 109
Solution
Dynamic planning
First Try(TLE on some testcase):
| |
Optimized by bisect
| |
| |
2273. Find Resultant Array After Removing Anagrams 2025.10.13
You are given a 0-indexed string array words, where words[i] consists of lowercase English letters.
In one operation, select any index i such that 0 < i < words.length and words[i - 1] and words[i] are anagrams, and delete words[i] from words. Keep performing this operation as long as you can select an index that satisfies the conditions.
Return words after performing all operations. It can be shown that selecting the indices for each operation in any arbitrary order will lead to the same result.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase using all the original letters exactly once. For example, "dacb" is an anagram of "abdc".
Example 1:
Input: words = [“abba”,“baba”,“bbaa”,“cd”,“cd”]
Output: [“abba”,“cd”]
Explanation:
One of the ways we can obtain the resultant array is by using the following operations:
- Since words[2] = “bbaa” and words[1] = “baba” are anagrams, we choose index 2 and delete words[2].
Now words = [“abba”,“baba”,“cd”,“cd”]. - Since words[1] = “baba” and words[0] = “abba” are anagrams, we choose index 1 and delete words[1].
Now words = [“abba”,“cd”,“cd”]. - Since words[2] = “cd” and words[1] = “cd” are anagrams, we choose index 2 and delete words[2].
Now words = [“abba”,“cd”]. We can no longer perform any operations, so [“abba”,“cd”] is the final answer.
Example 2:
Input: words = [“a”,“b”,“c”,“d”,“e”]
Output: [“a”,“b”,“c”,“d”,“e”]
Explanation:
No two adjacent strings in words are anagrams of each other, so no operations are performed.
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 1001 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.
Solution
| |
| |
3349. Adjacent Increasing Subarrays Detection I 2025.10.14
Given an array nums of n integers and an integer k, determine whether there exist two adjacent subarrays of length k such that both subarrays are strictly increasing. Specifically, check if there are two subarrays starting at indices a and b (a < b), where:
- Both subarrays
nums[a..a + k - 1]andnums[b..b + k - 1]are strictly increasing. - The subarrays must be adjacent, meaning
b = a + k.
Return true if it is possible to find two such subarrays, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,7,8,9,2,3,4,3,1], k = 3
Output: true
Explanation:
- The subarray starting at index
2is[7, 8, 9], which is strictly increasing. - The subarray starting at index
5is[2, 3, 4], which is also strictly increasing. - These two subarrays are adjacent, so the result is
true.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,4,4,4,5,6,7], k = 5
Output: false
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 1001 < 2 * k <= nums.length-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
Solution
| |
3350. Adjacent Increasing Subarrays Detection II 2025.10.15
Given an array nums of n integers, your task is to find the maximum value of k for which there exist two adjacent subarrays of length k each, such that both subarrays are strictly increasing. Specifically, check if there are two subarrays of length k starting at indices a and b (a < b), where:
- Both subarrays
nums[a..a + k - 1]andnums[b..b + k - 1]are strictly increasing. - The subarrays must be adjacent, meaning
b = a + k.
Return the maximum possible value of k.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,7,8,9,2,3,4,3,1]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- The subarray starting at index 2 is
[7, 8, 9], which is strictly increasing. - The subarray starting at index 5 is
[2, 3, 4], which is also strictly increasing. - These two subarrays are adjacent, and 3 is the maximum possible value of
kfor which two such adjacent strictly increasing subarrays exist.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,4,4,4,5,6,7]
Output: 2
Explanation:
- The subarray starting at index 0 is
[1, 2], which is strictly increasing. - The subarray starting at index 2 is
[3, 4], which is also strictly increasing. - These two subarrays are adjacent, and 2 is the maximum possible value of
kfor which two such adjacent strictly increasing subarrays exist.
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 2 * 105-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
Solution
| |
2598. Smallest Missing Non-negative Integer After Operations 2025.10.16
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and an integer value.
In one operation, you can add or subtract value from any element of nums.
- For example, if
nums = [1,2,3]andvalue = 2, you can choose to subtractvaluefromnums[0]to makenums = [-1,2,3].
The MEX (minimum excluded) of an array is the smallest missing non-negative integer in it.
- For example, the MEX of
[-1,2,3]is0while the MEX of[1,0,3]is2.
Return the maximum MEX of nums after applying the mentioned operation any number of times.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-10,7,13,6,8], value = 5
Output: 4
Explanation: One can achieve this result by applying the following operations:
- Add value to nums[1] twice to make nums = [1,0,7,13,6,8]
- Subtract value from nums[2] once to make nums = [1,0,2,13,6,8]
- Subtract value from nums[3] twice to make nums = [1,0,2,3,6,8] The MEX of nums is 4. It can be shown that 4 is the maximum MEX we can achieve.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,-10,7,13,6,8], value = 7
Output: 2
Explanation: One can achieve this result by applying the following operation:
- subtract value from nums[2] once to make nums = [1,-10,0,13,6,8] The MEX of nums is 2. It can be shown that 2 is the maximum MEX we can achieve.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length, value <= 105-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
Solution
| |
3461. Check If Digits Are Equal in String After Operations I 2025.10.23
You are given a string s consisting of digits. Perform the following operation repeatedly until the string has exactly two digits:
- For each pair of consecutive digits in
s, starting from the first digit, calculate a new digit as the sum of the two digits modulo 10. - Replace
swith the sequence of newly calculated digits, maintaining the order in which they are computed.
Return true if the final two digits in s are the same; otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: s = “3902”
Output: true
Explanation:
- Initially,
s = "3902" - First operation:
(s[0] + s[1]) % 10 = (3 + 9) % 10 = 2(s[1] + s[2]) % 10 = (9 + 0) % 10 = 9(s[2] + s[3]) % 10 = (0 + 2) % 10 = 2sbecomes"292"
- Second operation:
(s[0] + s[1]) % 10 = (2 + 9) % 10 = 1(s[1] + s[2]) % 10 = (9 + 2) % 10 = 1sbecomes"11"
- Since the digits in
"11"are the same, the output istrue.
Example 2:
Input: s = “34789”
Output: false
Explanation:
- Initially,
s = "34789". - After the first operation,
s = "7157". - After the second operation,
s = "862". - After the third operation,
s = "48". - Since
'4' != '8', the output isfalse.
Constraints:
3 <= s.length <= 100sconsists of only digits.
Solution
| |
2048. Next Greater Numerically Balanced Number 2025.10.24
An integer x is numerically balanced if for every digit d in the number x, there are exactly d occurrences of that digit in x.
Given an integer n, return the smallest numerically balanced number strictly greater than n.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1
Output: 22
Explanation:
22 is numerically balanced since:
- The digit 2 occurs 2 times. It is also the smallest numerically balanced number strictly greater than 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1000
Output: 1333
Explanation:
1333 is numerically balanced since:
- The digit 1 occurs 1 time.
- The digit 3 occurs 3 times.
It is also the smallest numerically balanced number strictly greater than 1000. Note that 1022 cannot be the answer because 0 appeared more than 0 times.
Example 3:
Input: n = 3000
Output: 3133
Explanation:
3133 is numerically balanced since:
- The digit 1 occurs 1 time.
- The digit 3 occurs 3 times. It is also the smallest numerically balanced number strictly greater than 3000.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 106
| |
1716. Calculate Money in Leetcode Bank 2025.10.25
Hercy wants to save money for his first car. He puts money in the Leetcode bank every day.
He starts by putting in $1 on Monday, the first day. Every day from Tuesday to Sunday, he will put in $1 more than the day before. On every subsequent Monday, he will put in $1 more than the previous Monday.
Given n, return the total amount of money he will have in the Leetcode bank at the end of the nth day.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4
Output: 10
Explanation: After the 4th day, the total is 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10.
Example 2:
Input: n = 10
Output: 37
Explanation: After the 10th day, the total is (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7) + (2 + 3 + 4) = 37. Notice that on the 2nd Monday, Hercy only puts in $2.
Example 3:
Input: n = 20
Output: 96
Explanation: After the 20th day, the total is (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7) + (2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8) + (3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8) = 96.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000
Solution
| |
2125. Number of Laser Beams in a Bank 2025.10.27
Anti-theft security devices are activated inside a bank. You are given a 0-indexed binary string array bank representing the floor plan of the bank, which is an m x n 2D matrix. bank[i] represents the ith row, consisting of '0's and '1's. '0' means the cell is empty, while'1' means the cell has a security device.
There is one laser beam between any two security devices if both conditions are met:
- The two devices are located on two different rows:
r1andr2, wherer1 < r2. - For each row
iwherer1 < i < r2, there are no security devices in theithrow.
Laser beams are independent, i.e., one beam does not interfere nor join with another.
Return the total number of laser beams in the bank.
Example 1:
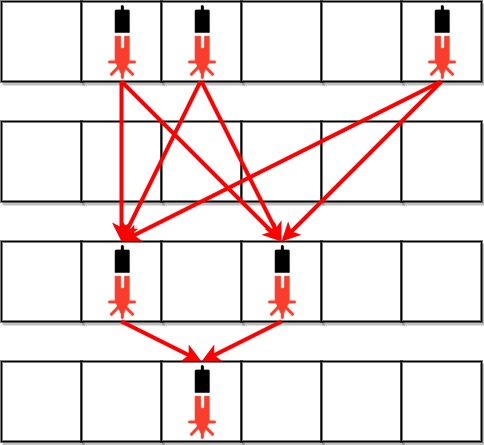
Input: bank = [“011001”,“000000”,“010100”,“001000”]
Output: 8
Explanation: Between each of the following device pairs, there is one beam. In total, there are 8 beams:
- bank[0][1] – bank[2][1]
- bank[0][1] – bank[2][3]
- bank[0][2] – bank[2][1]
- bank[0][2] – bank[2][3]
- bank[0][5] – bank[2][1]
- bank[0][5] – bank[2][3]
- bank[2][1] – bank[3][2]
- bank[2][3] – bank[3][2] Note that there is no beam between any device on the 0th row with any on the 3rd row. This is because the 2nd row contains security devices, which breaks the second condition.
Example 2:
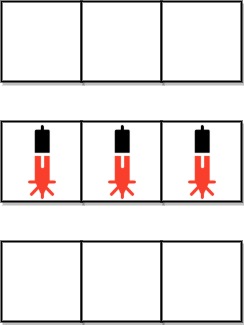
Input: bank = [“000”,“111”,“000”]
Output: 0
Explanation: There does not exist two devices located on two different rows.
Constraints:
m == bank.lengthn == bank[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500bank[i][j]is either'0'or'1'.
Solution
| |
3370. Smallest Number With All Set Bits 2025.10.29
You are given a positive number n.
Return the smallest number x greater than or equal to n, such that the binary representation of x contains only set bits
Example 1:
Input: n = 5
Output: 7
Explanation:
The binary representation of 7 is "111".
Example 2:
Input: n = 10
Output: 15
Explanation:
The binary representation of 15 is "1111".
Example 3:
Input: n = 3
Output: 3
Explanation:
The binary representation of 3 is "11".
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000
Solution
- Bisect, low efficiency
| |
- Construct bit by bit
| |
- Bit operation (most efficient)
| |
3289. The Two Sneaky Numbers of Digitville 2025.10.31
In the town of Digitville, there was a list of numbers called nums containing integers from 0 to n - 1. Each number was supposed to appear exactly once in the list, however, two mischievous numbers sneaked in an additional time, making the list longer than usual.
As the town detective, your task is to find these two sneaky numbers. Return an array of size two containing the two numbers (in any order), so peace can return to Digitville.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,1,1,0]
Output: [0,1]
Explanation:
The numbers 0 and 1 each appear twice in the array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,2,1,3,2]
Output: [2,3]
Explanation:
The numbers 2 and 3 each appear twice in the array.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [7,1,5,4,3,4,6,0,9,5,8,2]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
The numbers 4 and 5 each appear twice in the array.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 100nums.length == n + 20 <= nums[i] < n- The input is generated such that
numscontains exactly two repeated elements.
Solution
| |
3217. Delete Nodes From Linked List Present in Array 2025.11.01
You are given an array of integers nums and the head of a linked list. Return the head of the modified linked list after removing all nodes from the linked list that have a value that exists in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
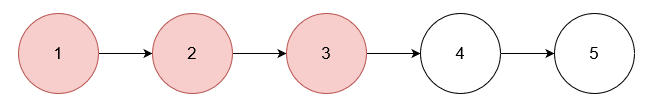
Remove the nodes with values 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1], head = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
Output: [2,2,2]
Explanation:
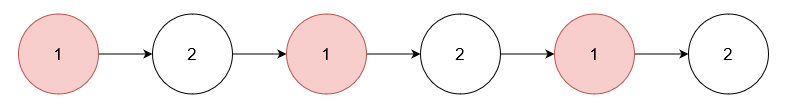
Remove the nodes with value 1.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5], head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
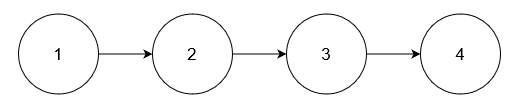
No node has value 5.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105- All elements in
numsare unique. - The number of nodes in the given list is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- The input is generated such that there is at least one node in the linked list that has a value not present in
nums.
Solution
| |
2257. Count Unguarded Cells in the Grid 2025.11.02
You are given two integers m and n representing a 0-indexed m x n grid. You are also given two 2D integer arrays guards and walls where guards[i] = [rowi, coli] and walls[j] = [rowj, colj] represent the positions of the ith guard and jth wall respectively.
A guard can see every cell in the four cardinal directions (north, east, south, or west) starting from their position unless obstructed by a wall or another guard. A cell is guarded if there is at least one guard that can see it.
Return the number of unoccupied cells that are not guarded.
Example 1:
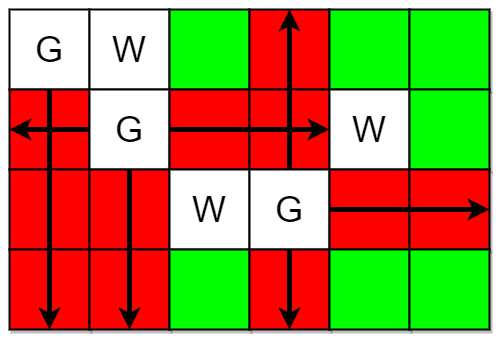
Input: m = 4, n = 6, guards = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,3]], walls = [[0,1],[2,2],[1,4]]
Output: 7
Explanation: The guarded and unguarded cells are shown in red and green respectively in the above diagram.
There are a total of 7 unguarded cells, so we return 7.
Example 2:
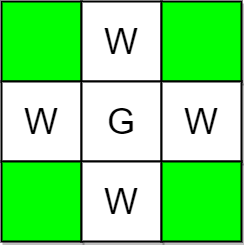
Input: m = 3, n = 3, guards = [[1,1]], walls = [[0,1],[1,0],[2,1],[1,2]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The unguarded cells are shown in green in the above diagram.
There are a total of 4 unguarded cells, so we return 4.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 1052 <= m * n <= 1051 <= guards.length, walls.length <= 5 * 1042 <= guards.length + walls.length <= m * nguards[i].length == walls[j].length == 20 <= rowi, rowj < m0 <= coli, colj < n- All the positions in
guardsandwallsare unique.
Solution
| |
3623. Count Number of Trapezoids I
You are given a 2D integer array points, where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents the coordinates of the ith point on the Cartesian plane.
A horizontal trapezoid is a convex quadrilateral with at least one pair of horizontal sides (i.e. parallel to the x-axis). Two lines are parallel if and only if they have the same slope.
Return the number of unique horizontal trapezoids that can be formed by choosing any four distinct points from points.
Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: points = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,0],[2,2],[3,2]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
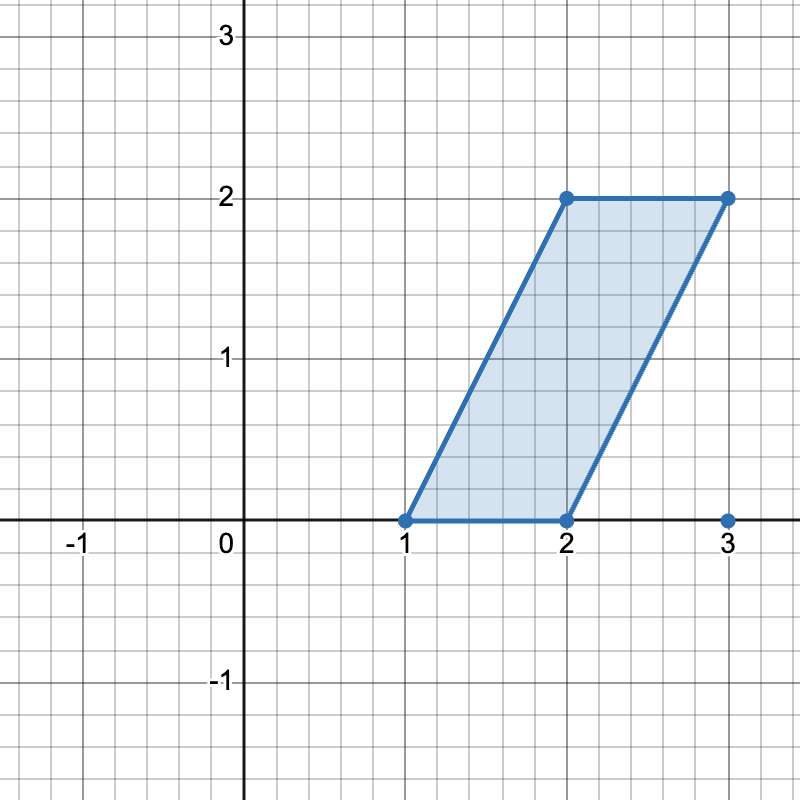
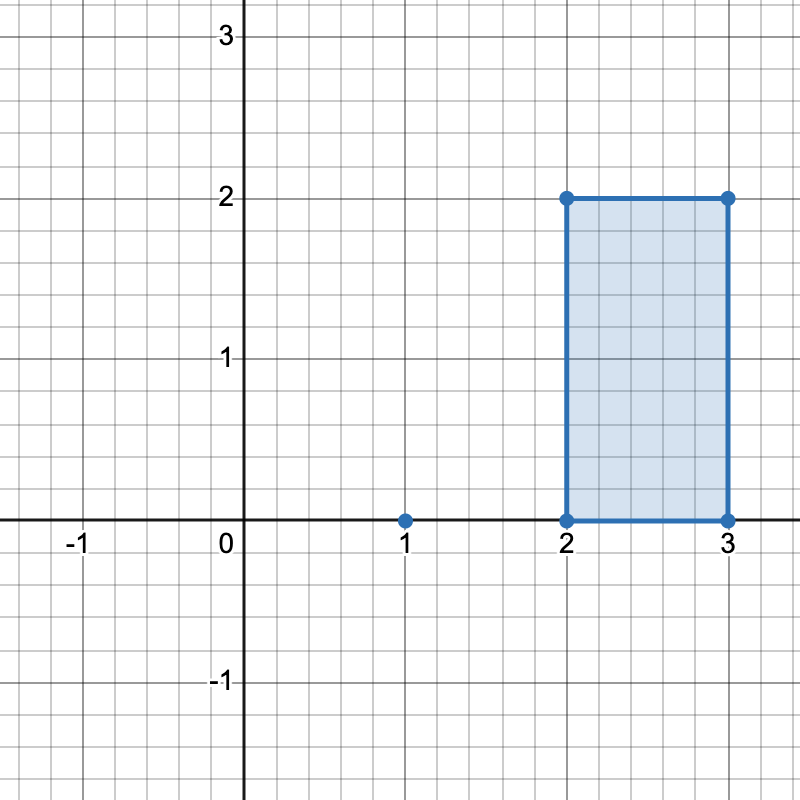
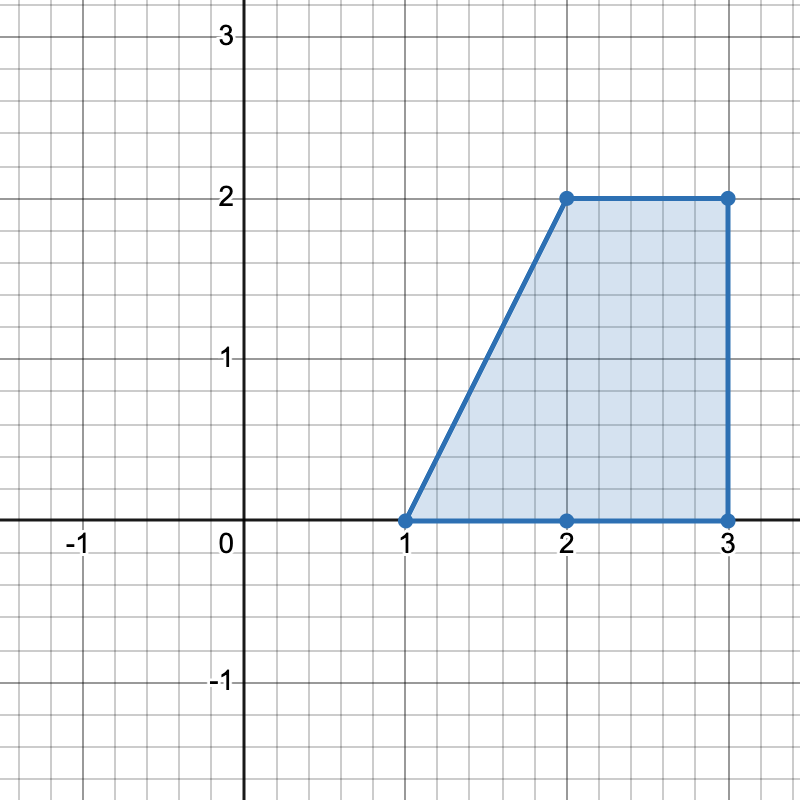
There are three distinct ways to pick four points that form a horizontal trapezoid:
- Using points
[1,0],[2,0],[3,2], and[2,2]. - Using points
[2,0],[3,0],[3,2], and[2,2]. - Using points
[1,0],[3,0],[3,2], and[2,2].
Example 2:
Input: points = [[0,0],[1,0],[0,1],[2,1]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
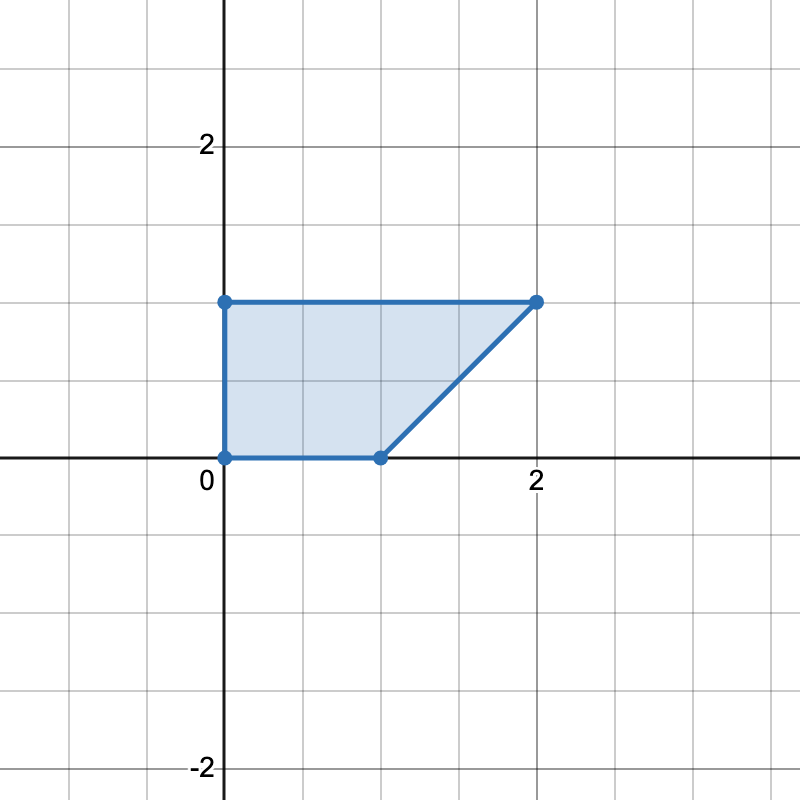
There is only one horizontal trapezoid that can be formed.
Constraints:
4 <= points.length <= 105–108 <= xi, yi <= 108- All points are pairwise distinct.
Solution
| |
2211. Count Collisions on a Road
There are n cars on an infinitely long road. The cars are numbered from 0 to n - 1 from left to right and each car is present at a unique point.
You are given a 0-indexed string directions of length n. directions[i] can be either 'L', 'R', or 'S' denoting whether the ith car is moving towards the left, towards the right, or staying at its current point respectively. Each moving car has the same speed.
The number of collisions can be calculated as follows:
- When two cars moving in opposite directions collide with each other, the number of collisions increases by
2. - When a moving car collides with a stationary car, the number of collisions increases by
1.
After a collision, the cars involved can no longer move and will stay at the point where they collided. Other than that, cars cannot change their state or direction of motion.
Return the total number of collisions that will happen on the road.
Example 1:
Input: directions = “RLRSLL” Output: 5 Explanation: The collisions that will happen on the road are:
- Cars 0 and 1 will collide with each other. Since they are moving in opposite directions, the number of collisions becomes 0 + 2 = 2.
- Cars 2 and 3 will collide with each other. Since car 3 is stationary, the number of collisions becomes 2 + 1 = 3.
- Cars 3 and 4 will collide with each other. Since car 3 is stationary, the number of collisions becomes 3 + 1 = 4.
- Cars 4 and 5 will collide with each other. After car 4 collides with car 3, it will stay at the point of collision and get hit by car 5. The number of collisions becomes 4 + 1 = 5. Thus, the total number of collisions that will happen on the road is 5.
Example 2:
Input: directions = “LLRR” Output: 0 Explanation: No cars will collide with each other. Thus, the total number of collisions that will happen on the road is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= directions.length <= 105directions[i]is either'L','R', or'S'.
Solutions
First Try: Wrong Answer: failed to consider chain reactions
"SSRSSRLLRSLLRSRSSRLRRRRLLRRLSSRR" answer is 20
| |
Right answer: key insight: every ‘L’ on the left will not collide every ‘R’ on the right will not collide everything middle will eventually collides
| |
3432. Count Partitions with Even Sum Difference
You are given an integer array nums of length n.
A partition is defined as an index i where 0 <= i < n - 1, splitting the array into two non-empty subarrays such that:
- Left subarray contains indices
[0, i]. - Right subarray contains indices
[i + 1, n - 1].
Return the number of partitions where the difference between the sum of the left and right subarrays is even.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [10,10,3,7,6]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The 4 partitions are:
[10],[10, 3, 7, 6]with a sum difference of10 - 26 = -16, which is even.[10, 10],[3, 7, 6]with a sum difference of20 - 16 = 4, which is even.[10, 10, 3],[7, 6]with a sum difference of23 - 13 = 10, which is even.[10, 10, 3, 7],[6]with a sum difference of30 - 6 = 24, which is even.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,2]
Output: 0
Explanation:
No partition results in an even sum difference.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,4,6,8]
Output: 3
Explanation:
All partitions result in an even sum difference.
Constraints:
2 <= n == nums.length <= 1001 <= nums[i] <= 100
Solution
If the sum of nums is even, it can be split to odd+odd or even+even with even difference. If the sum of nums if odd, it can be split to odd+even with difference that can’t be even.
| |
| |
1523. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range
Given two non-negative integers low and high. Return the count of odd numbers between low and high (inclusive).
Example 1:
Input: low = 3, high = 7
Output: 3
Explanation: The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].
Example 2:
Input: low = 8, high = 10
Output: 1
Explanation: The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].
Constraints:
0 <= low <= high <= 10^9
Solution
| |
1925. Count Square Sum Triples
A square triple (a,b,c) is a triple where a, b, and c are integers and a^2 + b^2 = c^2.
Given an integer n, return the number of square triples such that 1 <= a, b, c <= n.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5
Output: 2
Explanation: The square triples are (3,4,5) and (4,3,5).
Example 2:
Input: n = 10
Output: 4
Explanation: The square triples are (3,4,5), (4,3,5), (6,8,10), and (8,6,10).
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 250
Solution
| |
3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
You are given an array complexity of length n.
There are n locked computers in a room with labels from 0 to n - 1, each with its own unique password. The password of the computer i has a complexity complexity[i].
The password for the computer labeled 0 is already decrypted and serves as the root. All other computers must be unlocked using it or another previously unlocked computer, following this information:
- You can decrypt the password for the computer
iusing the password for computerj, wherejis any integer less thaniwith a lower complexity. (i.e.j < iandcomplexity[j] < complexity[i]) - To decrypt the password for computer
i, you must have already unlocked a computerjsuch thatj < iandcomplexity[j] < complexity[i].
Find the number of permutations of [0, 1, 2, ..., (n - 1)] that represent a valid order in which the computers can be unlocked, starting from computer 0 as the only initially unlocked one.
Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Note that the password for the computer with label 0 is decrypted, and not the computer with the first position in the permutation.
Example 1:
Input: complexity = [1,2,3]
Output: 2
Explanation:
The valid permutations are:
- [0, 1, 2]
- Unlock computer 0 first with root password.
- Unlock computer 1 with password of computer 0 since
complexity[0] < complexity[1]. - Unlock computer 2 with password of computer 1 since
complexity[1] < complexity[2].
- [0, 2, 1]
- Unlock computer 0 first with root password.
- Unlock computer 2 with password of computer 0 since
complexity[0] < complexity[2]. - Unlock computer 1 with password of computer 0 since
complexity[0] < complexity[1].
Example 2:
Input: complexity = [3,3,3,4,4,4]
Output: 0
Explanation:
There are no possible permutations which can unlock all computers.
Constraints:
2 <= complexity.length <= 1051 <= complexity[i] <= 109
Solution
| |
3531. Count Covered Buildings
You are given a positive integer n, representing an n x n city. You are also given a 2D grid buildings, where buildings[i] = [x, y] denotes a unique building located at coordinates [x, y].
A building is covered if there is at least one building in all four directions: left, right, above, and below.
Return the number of covered buildings.
Example 1:
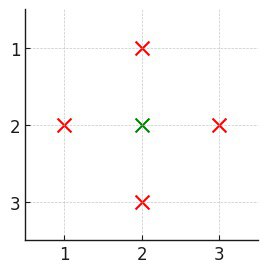
Input: n = 3, buildings = [[1,2],[2,2],[3,2],[2,1],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
- Only building
[2,2]is covered as it has at least one building:- above (
[1,2]) - below (
[3,2]) - left (
[2,1]) - right (
[2,3])
- above (
- Thus, the count of covered buildings is 1.
Example 2:
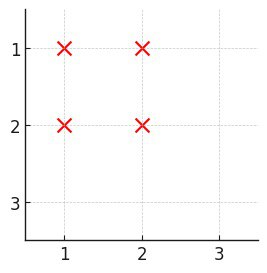
Input: n = 3, buildings = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
- No building has at least one building in all four directions.
Example 3:

Input: n = 5, buildings = [[1,3],[3,2],[3,3],[3,5],[5,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
- Only building
[3,3]is covered as it has at least one building:- above (
[1,3]) - below (
[5,3]) - left (
[3,2]) - right (
[3,5])
- above (
- Thus, the count of covered buildings is 1.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1051 <= buildings.length <= 105buildings[i] = [x, y]1 <= x, y <= n- All coordinates of
buildingsare unique.
Solution
| |
3606. Coupon Code Validator
You are given three arrays of length n that describe the properties of n coupons: code, businessLine, and isActive. The ith coupon has:
code[i]: a string representing the coupon identifier.businessLine[i]: a string denoting the business category of the coupon.isActive[i]: a boolean indicating whether the coupon is currently active.
A coupon is considered valid if all of the following conditions hold:
code[i]is non-empty and consists only of alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and underscores (_).businessLine[i]is one of the following four categories:"electronics","grocery","pharmacy","restaurant".isActive[i]is true.
Return an array of the codes of all valid coupons, sorted first by their businessLine in the order: "electronics", "grocery", "pharmacy", "restaurant", and then by code in lexicographical (ascending) order within each category.
Example 1:
Input: code = [“SAVE20”,"",“PHARMA5”,“SAVE@20”], businessLine = [“restaurant”,“grocery”,“pharmacy”,“restaurant”], isActive = [true,true,true,true]
Output: [“PHARMA5”,“SAVE20”]
Explanation:
- First coupon is valid.
- Second coupon has empty code (invalid).
- Third coupon is valid.
- Fourth coupon has special character
@(invalid).
Example 2:
Input: code = [“GROCERY15”,“ELECTRONICS_50”,“DISCOUNT10”], businessLine = [“grocery”,“electronics”,“invalid”], isActive = [false,true,true]
Output: [“ELECTRONICS_50”]
Explanation:
- First coupon is inactive (invalid).
- Second coupon is valid.
- Third coupon has invalid business line (invalid).
Constraints:
n == code.length == businessLine.length == isActive.length1 <= n <= 1000 <= code[i].length, businessLine[i].length <= 100code[i]andbusinessLine[i]consist of printable ASCII characters.isActive[i]is eithertrueorfalse.
Solution
| |
2110. Number of Smooth Descent Periods of a Stock
You are given an integer array prices representing the daily price history of a stock, where prices[i] is the stock price on the ith day.
A smooth descent period of a stock consists of one or more contiguous days such that the price on each day is lower than the price on the preceding day by exactly 1. The first day of the period is exempted from this rule.
Return the number of smooth descent periods.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [3,2,1,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: There are 7 smooth descent periods:
[3], [2], [1], [4], [3,2], [2,1], and [3,2,1]
Note that a period with one day is a smooth descent period by the definition.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [8,6,7,7]
Output: 4
Explanation: There are 4 smooth descent periods: [8], [6], [7], and [7]
Note that [8,6] is not a smooth descent period as 8 - 6 ≠ 1.
Example 3:
Input: prices = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: There is 1 smooth descent period: [1]
Constraints:
1 <= prices.length <= 1051 <= prices[i] <= 105
Solution
| |
3573. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock V
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a stock in dollars on the ith day, and an integer k.
You are allowed to make at most k transactions, where each transaction can be either of the following:
Normal transaction: Buy on day
i, then sell on a later dayjwherei < j. You profitprices[j] - prices[i].Short selling transaction: Sell on day
i, then buy back on a later dayjwherei < j. You profitprices[i] - prices[j].
Note that you must complete each transaction before starting another. Additionally, you can’t buy or sell on the same day you are selling or buying back as part of a previous transaction.
Return the maximum total profit you can earn by making at most k transactions.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [1,7,9,8,2], k = 2
Output: 14
Explanation:
We can make $14 of profit through 2 transactions:
- A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 0 for
$1 then sell it on day 2 for$9. - A short selling transaction: sell the stock on day 3 for
$8 then buy back on day 4 for$2.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [12,16,19,19,8,1,19,13,9], k = 3
Output: 36
Explanation:
We can make $36 of profit through 3 transactions:
- A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 0 for
$12 then sell it on day 2 for$19. - A short selling transaction: sell the stock on day 3 for
$19 then buy back on day 4 for$8. - A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 5 for
$1 then sell it on day 6 for$19.
Constraints:
2 <= prices.length <= 1031 <= prices[i] <= 1091 <= k <= prices.length / 2
Solution
| |