Janvier#
Given an integer array nums, return the sum of divisors of the integers in that array that have exactly four divisors. If there is no such integer in the array, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [21,4,7]
Output: 32
Explanation:
21 has 4 divisors: 1, 3, 7, 21
4 has 3 divisors: 1, 2, 4
7 has 2 divisors: 1, 7
The answer is the sum of divisors of 21 only.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [21,21]
Output: 64
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^41 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution:
def numDivisor(self, num: int) -> int:
if abs(int(sqrt(num))-sqrt(num)) < 1e-9:
return 0
tot = 0
count = 0
for i in range(1, int(sqrt(num))+1):
if num % i == 0:
count += 2
tot += i
tot += num // i
if count > 4:
return 0
return tot if count == 4 else 0
def sumFourDivisors(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = 0
for num in nums:
res += self.numDivisor(num)
return res
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Solution {
public:
int sumFourDivisors(vector<int>& nums) {
int res {0};
for(int i: nums){
res += numDivisor(i);
cout << numDivisor(i) << endl;
}
return res;
}
int numDivisor(int num){
int r = sqrt(num);
if(r * r == num) return 0;
int tot {0};
int count {0};
for(int i=1;i<sqrt(num);++i){
if(num % i == 0){
count += 2;
if(count > 4) return 0;
tot += i;
tot += num / i;
}
}
if(count == 4) return tot;
else return 0;
}
};
|
You are given an n x n integer matrix. You can do the following operation any number of times:
- Choose any two adjacent elements of
matrix and multiply each of them by -1.
Two elements are considered adjacent if and only if they share a border.
Your goal is to maximize the summation of the matrix’s elements. Return the maximum sum of the matrix’s elements using the operation mentioned above.
Example 1:
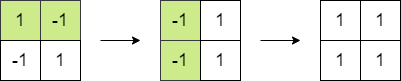
Input: matrix = [[1,-1],[-1,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: We can follow the following steps to reach sum equals 4:
- Multiply the 2 elements in the first row by -1.
- Multiply the 2 elements in the first column by -1.
Example 2:
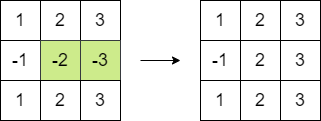
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[-1,-2,-3],[1,2,3]]
Output: 16
Explanation: We can follow the following step to reach sum equals 16:
- Multiply the 2 last elements in the second row by -1.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length2 <= n <= 250-105 <= matrix[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution
If the number of negative elements is even, we can always make it positive.
If the number is odd, we can always choose the smallest absolute value to make it negative.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution:
def maxMatrixSum(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
tot = 0
minVal = 1e5+1
count = 0
n = len(matrix)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
minVal = min(minVal, abs(matrix[i][j]))
tot += abs(matrix[i][j])
if matrix[i][j] < 0:
count += 1
return tot if (count % 2 == 0) else (tot - 2 * minVal)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
long long maxMatrixSum(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
long long tot {0};
int count {0};
int minVal {INT_MAX};
for(size_t i=0;i<matrix.size();++i){
for(size_t j=0;j<matrix.size();++j){
tot += abs(matrix[i][j]);
minVal = min(minVal, abs(matrix[i][j]));
if (matrix[i][j] < 0) count += 1;
}
}
if(count % 2 == 0) return tot;
else return tot - 2 * minVal;
}
};
|
Given the root of a binary tree, the level of its root is 1, the level of its children is 2, and so on.
Return the smallest level x such that the sum of all the values of nodes at level x is maximal.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,7,0,7,-8,null,null]
Output: 2
Explanation:
Level 1 sum = 1.
Level 2 sum = 7 + 0 = 7.
Level 3 sum = 7 + -8 = -1.
So we return the level with the maximum sum which is level 2.
Example 2:
Input: root = [989,null,10250,98693,-89388,null,null,null,-32127]
Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution
Loop by hierarchy and compare
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxLevelSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
curr_level = [root, ]
max_sum = root.val
max_level = 1
level = 1
while curr_level:
next_level = list()
curr_sum = 0
for node in curr_level:
curr_sum += node.val
if node.left:
next_level.append(node.left)
if node.right:
next_level.append(node.right)
if curr_sum > max_sum:
max_sum = curr_sum
max_level = level
curr_level = next_level
level += 1
return max_level
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxLevelSum(TreeNode* root) {
int max_sum {root->val};
int max_level {1};
int level {1};
vector<TreeNode*> curr_level {root};
while(!curr_level.empty()){
vector<TreeNode*> next_level;
int curr_sum {0};
for(TreeNode* node: curr_level){
curr_sum += node->val;
if(node->left) next_level.push_back(node->left);
if(node->right) next_level.push_back(node->right);
}
if(curr_sum > max_sum){
max_sum = curr_sum;
max_level = level;
}
curr_level = move(next_level);
level ++;
}
return max_level;
}
};
|


